You’re
Guide to Buying a Vehicle barriers
Whether
you need to enhance security at
a building or increase safety at a specific locale or job site, you will
need vehicle boom barriers to help you
achieve your goal. Access control is the mechanism that is used for
controlling, restricting and monitoring the movement of assets, vehicles and
people in or out any building. A drop arm Automatic Boom Barrier is commonly
used for controlling the unauthorized entries of any personnel while enforcing
access control system. It assures that one token one-person policy is followed
24 x 7. The levels of security that a boom barrier offers depends on style and
type of products being used. For example, if the Automatic boom barrier is used
with a lockable sliding gate, then it is easier to keep a check on each and
every person or vehicle entering. You should know that these are not meant to
be used as a pedestrian passage, as a boom barrier is a horizontal bar that is
positioned on a pivot that moves up and down. This technology can also be
integrated with other systems like visitor management, ANPR, CCTV, BMS and
more which eventually saves costs and offer better security services.
If you are
a system integrator or gate automation installer or even a gate barrier
distributor (like SSA Integrate), it is important to know how to select
the best gate barrier system on behalf of the customer. Majority of the
datasheets and catalogues are not really useful unless you already know what
you are getting into.
What
Are Vehicle Barriers?
Vehicle
barriers refer to any device that causes cars to slow down, usually
purposefully but not necessarily. They are most often used in areas with high
pedestrian traffic, especially when children and seniors make up a large
portion of that pedestrian traffic, such as schools/ roads zones.
However, you can find them in many places, including highway mediums, parking
lots, railroad crossings, commercial districts, private communities, and
construction sites.
What
Are Boom Barriers?
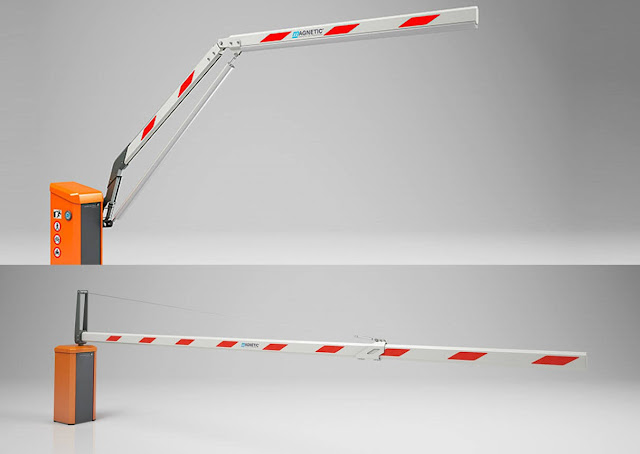
A boom
barrier, also known as a boom gate, is a bar, or pole pivoted to allow the
boom to block vehicular or pedestrian access through a controlled point.
Typically the tip of a boom gate rises in a vertical arc to a near vertical
position. Boom gates are often counterweighted, so the pole is easily tipped.
What
are the primary benefits of an Automatic boom barrier?
1. Enhanced Security:
Security is one of the most crucial things nowadays for
residential and commercial buildings. When there is boom barrier installed, the
gatekeeper can ensure that entry is given to the people based on their
credentials. If a particular vehicle is blacklisted from entering the premises,
then its entry can be easily blocked.
2. Traffic Flow can be Managed:
For controlling the flow of traffic on and off your property
boom gates are the best option. If your space has limited parking, then also
boom barrier can be a great help to maintain the number of vehicles. When the
parking is full, you can prevent any more vehicles from entering the premises.
3. Efficient Use of Space:
With a boom gate, you can make the efficient use of space
because installing sliding gates or swinging gates needs larger area. A boom
barrier requires a small amount of vertical space in order to swing upwards.
The most important thing is to get the boom barrier installed from a
service that does the job once and for all.
What
you should consider before buying a vehicle barrier?
At SSA Integrate, we always strive to
share our research and learnings with our customers and the gate automation
professional community. Here is our attempt to provide you with a checklist
that captures the essential questions and the likely answers to look for. This
guide must help you avoid the common mistakes and traps that the uninformed
fall into.
The questions are presented under
1. What is your use case?
2. What are the physical attributes?
3. How do you want to control access to the facility?
4. Safety features to consider
5. Additional features to consider
What
is your applications?
Before
purchasing a boom gate, one has to decide where it will be installed, and the
operating model. There are boom gates that are specifically designed for a
simple application like parking areas, traffic control to the large railway and
industrial crossings. It is necessary to understand the application, space
availability and use frequency.
If you are
system integrator ask Your
Customer
1.
Is it for commercial or industrial or residential
use?
2.
Is it for heavy traffic or low traffic area?
For high-frequency and limited
space
Buying a
barrier gate for under-ground or multistoried car parking lots presents the
challenge of limited space and high-frequency usage. Most of these structures
need continuous opening and closing of barrier gates. Some of the must-have
requirements for these facilities are – 100% duty cycle, arm articulation and
easy access control system integration.
Magnetic Access Pro barrier has 3.5m width boom and improved
opening and closing time, that can be adjusted to 1.3, 1.8, or 2.5 seconds
independently of one another.
For high frequency wider space
For
the installation at traffic junctions and toll gates on highways, there is a
requirement for barriers that support the lifting of extended boom lengths.
They are required to block access to tunnels and lanes but also to manage
traffic junctions with alternating traffic flows. Some of the must-have
features you should look for include – 100% duty cycle, Traffic lamp
integration, support for extended beam sizes.
Magnetic
Traffic H1 Horizontal Barrier has multiple application for high frequency wider
space.
Magnetic
Access XXL Barrier are excellent for extra-wide or multi-lane entrances and
comes with MHTM™ drive capability. With its barrier width of up to 10m and the
optional security grating or security grating with climb-over prevention Access
XXL offers range of functions.
Magnetic
Access XL2 Barrier are ideal for extra-wide or multi-lane entrances and comes
with optional security grating or security grating with climb-over prevention.
The opening and closing time for Access XL2 can be set at 6, 8, or 10 seconds independent
of one another.
For long life and energy
efficiency
Commercial
use barrier gates are used very frequently and require constant energy supply.
Two most important features required by the barriers operating in such
operational environments are long operational life and energy efficiency.
What is the duty cycle?
The duty
cycle for an automated gate operator is the number of times the gate can open
and close without overheating the motor. Duty cycle is normally expressed in
percentage. 100% duty cycle is meant for continuous use, eg: high intensive use
cases like a shopping mall, toll plaza etc.
There are
two most common categorisations: Residential (40-70% duty cycle) and commercial
(100% duty cycle). As you can imagine, a gate barrier in a mall will be used
much more time than one in an apartment. When calculating the required duty
cycle, calculate for the worst-case scenario.
If you are
system integrator ask Your
Customer
1.
What is the average usage (open/close cycle) per
day? (consider worst-case scenario)
What
is Barrier Operator?
Barrier
operators mostly come housed in the barrier body mounted on the floor or
foundation plate. The barrier operator usually comes with a motor that operates
on either hydraulic or electromechanical motors. Some latest products like FAAC
b680H also have hybrid motor technology with a Hydraulic Brushless motor in one
barrier operator. Hydraulic motors are usually more suitable for heavy-duty,
high frequency usage.
Hydraulic vs Electromechanical Motor
Hydraulic Motor
·
Hydraulic
controllers are very reliable and pose very few maintenance issues if installed
properly.
·
They
are a very effective deterrent in case a vehicle runs into the barrier or in
stopping tailgating vehicle.
·
Cold
can be a problem; too cold weather can cause oil thickening in the hydraulic
unit. However, this can be solved with a temperature control unit.
Electromechanical Motor
·
The
electromechanical unit is much quieter than the hydraulic motor.
·
A
bit slower than Hydraulic but they offer more control, one can set variable
speed for how quickly the beam rises.
·
Most
security professionals find the electro-mechanical unit easier to maintain.
·
The
Electro-mechanical units require at least 220v/single-phase power, which is
typically 12-15 more amps of power than what the hydraulic motor requires.
What
are the physical attributes
Arm length
Boom gates
come with different beam lengths and boom barrier shapes to suit the width of
the passage you wish to control. Beam length from 2 metres to 12 to 13 metres,
which are especially suitable for use when companies have oversized vehicles,
such as mine sites and rail crossings. They come in round or rectangular
shapes, wherein rectangular is a bit more expensive
If you are
Customer ask Your Vendor / System Integrator
1.
What is the drive-way width?
Arm articulation
Arm
articulation makes it possible to articulate the rigid beam to a maximum height
according to the ceiling. They are used in parking garages or in areas with
limited or low overhead clearances.
If you are
system integrator ask Your
Customer
1.
What is the height of the installation area or
overhead clearance available?
How
do you want to control
Barrier access control
Another
most important requirement you need to decide is how you want to control the
boom barrier – with reader, remote controller, or push button. They can be
configured with UHF readers and tags, with a control switch for security
officers, remote controllers and receivers, or with push buttons or biometrics.
Biometrics readers:
The
barriers can be controlled with biometric-readers like fingerprint, face,
Iris options.
Swipe Card Readers:
Access
control via RFID cards. Type: Magnetic, proximity cards, and proximity cards
with a magnetic stripe, key-chain FOB.
Support for GSM module:
This
module helps you open the gate barrier remotely by making a call to the SIM
inserted in the GSM module.
UHF readers & tags:
This
feature allows the barrier to be opened when a vehicle approaches the barrier
with authenticated tags.
Remote controller &
receiver:
The
barrier gates operated using the remote controller and a radio receiver
installed in the barrier.
Switch to Exit Button:
For
the facility security team to control the to and fro access.
If you are
system integrator ask Your
Customer
1.
What kind of access control is required to the
facility – biometric or remote or ANPR or RFID tag or swipe card based?
2. Is the
entry/exit point manned, does the security team need an exit button for the
manual opening?
Safety features to consider
Anti-crushing sensor
Gate boom
barriers feature safety components like sensors for automatic detection of
approaching vehicles, anti-crushing sensors that reverse the beam on impact if
the barrier boom automatically closes on the vehicle. The anti-crushing sensor
only stops repeated impact only after hitting the object once. That’s why you
need to have an additional detection mechanism in place – Photocells.
Photocells
Photocells
(motion sensors) are electronic devices that improve security by automatically
detecting vehicles or obstacles to enable automatic rising of booms. This
infrared setup will have a transmitter and receiver at each of the ends of the
driveway and whenever an obstacle is detected the barrier will prevent the gate
from closing and raise the barrier boom.
Micro Drive Break:
The
barriers can also be equipped with a flange set (FLVB02) is designed especially
for the parking industry. It enables the ejection of the whole barrier boom
after it was hit by a vehicle. The beam can be simply reinstalled after the
crash.
Loop detector
Barrier
gates come with other solutions like vehicle detection loops (inductive loop),
which are installed on the barrier that detects vehicles and passing or
arriving at a certain point. The loop detectors are connected to create a
magnetic field, and the vehicle is recognised when it enters this field.
Barrier
Housing
The
barrier housing is attached by four foundation anchors via two attachment
profiles. The housing of Magentic barrier is painted RAL 2000 and comes with an
IP 54 protection rating.
Battery
back-up
If you
want the barrier to operate even at the time of main power failure. Look for a
continuous duty cycle(in hours) supported by the battery backup.
Opening
and closing speed
Most
conventional barrier gates provide running speed from 1.5 seconds to 6 seconds.
If you are
system integrator ask Your
Customer
1. What is the
average opening time?
2.
Look for 1.5 seconds+
The
shape of the boom/beam
Magnetic
offers a variety of boom lengths, numerous extras like illumination elements
and expansion sets, allowing the tailored implementation of Magnetic barriers
for various uses. The booms come with skirt elements made of plastic and
aluminium, over-climb protection and break-away flange. The types of booms
offered include Varioboom, Microboom and Articulated booms. Also the round
booms and soft booms. SSA Integrate will guide you what actually you need.
Support
for modular beam/boom
What if
the barrier needs more length than the standard beam length? When there is
support for modular beams, the total length can be extended. Look for a boom
extension set.
Colour
of the gate barrier
Many
manufacturers support your preferred colour for the enclosure. Ask for the
supported colours.
International
standards or regulations
Look for
compliance with international standards (European/ISO) when it comes to safety
and quality.
Maintenance
and operating cost
You can
always buy a cheap gate barrier but watch out for maintenance and operating
cost. Operational cost is as important as the capital cost not just in terms of
money but the availability of spare parts and technicians.
Enclosure
rating
Gate
barriers are of course installed outside and the motors and the other internal
components should be protected from dust, water and other solid objects. Look
for the international standard Ingress Protection(IP) ratings like IP 54 or IP
56.
Temperature
Range
Again
consider the worst-case scenario, watch out for maximum and minimum temperature
tested and supported. Look for -20°C ÷ +55°C.
Integrated
flashing traffic light and reflector kit
These
optional modules help especially at night.
Anti-vandalism
valve or Anti-panic unit
Most
barriers come with safety features that stop forced opening or closing, and the
anti-vandalism valve protects the hydraulic system in case the beam is forced.
While an anti-panic unit is used for the manual opening of the barrier arm in
the event of a power failure. Since an anti-vandalism valve prevents
manual/forced movement of the beam, both anti-vandalism and anti-panic units
cannot be installed together in a barrier system.
Pedestals
The
pedestal is required when you need support for holding the access control
device. For truck entry gates you need a dual height pedestal while a single
height pedestal is used for car access. SSA Integrate will give you perfect
solution as per your needs.
Buyer’s
Checklist
You can
find a checklist with the most important questions below:-
|
Type
|
Value
|
|
Application
|
Is it for commercial or industrial or residential
use?
|
|
Is it for heavy traffic or low traffic area?
|
|
Duty Cycle
|
What is the average usage (open/close cycle) per
day?
|
|
Arm Length
|
What is the drive-way width?
|
|
Arm Articulation
|
What is the height of the installation area or
overhead clearance available?
|
|
Access Control
|
Is the entry/exit point manned, does the security
team need an exit button for the manual opening?
|
|
What kind of access control is required to the
facility – biometric or remote or ANPR or RFID tag or swipe card based?
|
|
Photocells
|
Do you need automatic detection of vehicles to
avoid collisions?
|
|
Loop detector
|
Do you need to automate vehicle exit?
|
|
Shape/Color
|
Do you need customised barriers?
|
|
Integrated flashing
light
|
Is there a need for integrated flashing light?
|
|
Reflector kit
|
Is the reflector kit included in the barrier
package?
|
|
Anti-vandalism valve
|
Is there a chance of forced operation?
|
|
Anti-panic
|
Manual opening in case of power supply failures?
|
|
Pedestals
|
What kind of vehicles are managed by the
entry/exit point? Trucks or Cars?
|
Complete
table of available accessories:-
|
Protocol
|
Access
|
Access Pro
|
Access L
|
Access Pro L
|
Access Pro H
|
Access XL2
|
Access XXL
|
Parking Pro
|
Magnetic Toll
|
|
Lane width up to 3.5m(toll 3.00m)
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
|
Lane width up to 5.0m
|
–
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
|
Lane width up to 6.0m
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
|
Lane width up to 8.5m
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
|
Lane width up to 10.0m
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
|
Usage with boom skirt
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
|
Variable I/O assignment
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
|
Fast opening speeds (<2.2 sec)
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
|
Variable opening times
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
|
Variable closing times
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
|
Network connection*
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
|
Integration of interfaces in the future
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
|
Low ceiling height (articulated boom)
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
|
Parallel operation
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
|
Advertising space in barrier boom
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
|
Usage with pedestrian traffic
|
✔
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
|
One standard colours
|
✔
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
|
Three standard colours
|
–
|
✔
|
–
|
✔
|
✔
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
|
Special colours optionally available
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|