Risk Assessment & Quality Control Procedure For Access Control System
A security risk assessment plays a critical role in evaluating the vulnerabilities and potential risks associated with access control systems. Our expertise in premises security allows us to assist organizations in identifying, analyzing, and implementing effective security controls to safeguard their assets.
When conducting a risk assessment, several factors come into play, including the size of the organization, its growth rate, available resources, and the nature of its asset portfolio. By conducting a comprehensive security assessment, we help organizations identify their critical assets, assess potential risks, implement mitigating controls, and proactively prevent threats and vulnerabilities.
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and government have specific regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and Sarbanes-Oxley Audit Standard 5, that mandate security risk assessments. With our expertise, we can ensure that your organization complies with these regulations while enhancing the overall security of your access control systems.
Quality Control Procedure For Access Control System
1.0 SCOPE: .
This procedure applies to all
the inspection activities related to monitoring and measurement of products and
Processes related for the Installation or testing of subject activity where
applicable for the project and Applicable to:
·
Method Statement.
·
Quality Control Procedure.
·
Inspection and Test Plans.
·
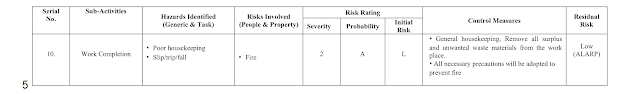
Risk Assessments
·
FORMS.
2.0 PURPOSE:
The purpose of this procedure is to :
o
Identify processes /
products those are to be installed before using them in intended application.
o
Define the methods to
verify the quality of products and ensure that products that meet the stated
requirements are only used in the intended application.
o
Define the
responsibilities of concerned personnel related to quality control processes.
3.0 REFERENCES
Project Quality Plan
Material Approvals
4.0 DEFINITIONS:
PQP : Project
Quality Plan.
PSP : Project Safety Plan.
QCP : Quality Control Procedure.
HSE : Health, Safety and Environment
MS : Method Statement
ITP : Inspection Test Plan
QA/QC : Quality Assurance / Quality Control
Engineer.
SK : Store Keeper
WIR : Work Inspection Request
MIR : Material Inspection Request.
MAR : Material Approval Request
5.0
RESPONSIBILITIES:
5.1 Project Manager
- Project Manager is the overall
responsible for the project in terms of work execution, safety, planning &
quality. The Project Manager will maintain the planning progress and
coordination of works with the main contractor.
-
The work progress shall be carried out as per
planned program and all the equipment’s required to execute the works shall be
available and in good condition as per project planned.
-
Specific attention is paid to all safety measures
and quality control in coordination with Safety Engineer and QA/QC Engineer and
in line with PSP and PQP.
5.2 Construction Manager
-
Construction Manager is responsible to supervise
and control the work on site.
-
Coordinating with QA/QC Engineer and site Team
and foremen for all activities on site.
-
Control and sign all WIR’s before issuing to Consultant
approval.
5.3 Site Engineer
-
The method of statement to the system shall be
implemented according to the Consultant project specifications and approved
shop drawings.
-
Provision of all necessary information and
distribution of responsibilities to his Construction team.
-
The work progress shall be monitored in
accordance with the planned work program and he will provide reports to his
superiors.
-
The constant coordination with the Safety
Engineer to ensure that the works are carried out in safe working atmosphere.
-
The constant coordination with the QA/QC Engineer
for any works to be carried out and initiate for the Inspection for the
finished works.
-
He will ensure the implementation of any request
that might be raised by the Consultant.
-
Efficient daily progress shall be obtained for
all the equipment and manpower.
-
He will engage in the work and check the same
against the daily report received from the Foremen.
-
The passage of all the revised information to the
Foremen and ensure that it’s being carried out properly.
5.4 QA/QC Engineer (MEP):
-
The monitoring of executions of works at site and
should be as per the approved shop drawings and project specifications.
-
Ensure WIRs and MIRs are being raised for
activities in timely manner and inspected by the Consultant.
-
Check and insure that all activities / work done
/ completed prior to offer for consultant inspection.
-
He will follow and carried out all the relevant
tests as per project specifications.
-
Obtain the required clearance prior to Consultant’s
inspections.
-
Should acquire any necessary civil works
clearances and coordination.
-
Coordinate with site construction team.
-
One who will assist the Consultant Engineer /
Inspector during inspection.
5.5 Site Foreman
-
The carrying-out of work and the proper
distribution of all the available resources in coordination with the Site
Engineer on a daily basis.
-
Daily reports of the works are achieved and
coordinated for the future planning with the Site Engineer.
-
Incorporate all the QA/QC and Safety requirements
as requested by the concerned Engineer.
-
Meeting with any type of unforeseen incident or
requirement and reporting the same to the Site Engineer immediately.
5.6 Safety Officer
-
The implementation of all safety measures in
accordance with the HSE plan and that the whole work force is aware of its
proper implementation.
-
The implementation of safety measures is adequate
to maintain a safe working environment on the work activity.
-
Inspection of all the site activities and
training personnel in accident prevention and its proper reporting to the
Construction Manager and the Project Manager.
-
The site is maintained in a clean and tidy
manner.
-
Ensure only trained persons shall operate the
power tools.
-
Ensure all concerned personals shall use PPE and
all other items as required.
-
Ensure adequate lighting is provided in the
working area at night time.
-
Ensure high risk elevated areas are provided are
barricade, tape, safety nets and provided with ladders.
-
Ensure service area/inspection area openings are
provided with barricade, tape, and safety nets.
- Ensure safe access to site work at all times.
5.8 Store Keeper (SK)
- Responsible
for overall Store operations in making sure to store the material delivery to
the site and keep it in suitable area that will keep the material in safe from
rusty and damage.
- One who will
acknowledge the receiving of materials at site in coordination with QA/QC and
concerned Engineer.
5.9 Emergency Absents
-
If QA/QC not available the adequate QA/QC Engineer
will be responsible for quality control activities.
-
If the P.M. not available the Construcion manager
will be resposible for all of his activities.
-
If the HSE Engineer not available the adequate HSE
Engineer are resposible for safety activities.
-
If Engineer not available Construction manager will
assign his duties to the concerned supervisor, forman or alternate Engineer.
-
Replacing staff, in case of absent, with another
designation can be accepted only for a minimum period of days absent otherwise
the Contractor shall replace the relevant person with same designation which
required approval from CONSULTANT.
6.0 PROCEDURE:
-
Check that all the following documentations have
been approved by the Consultant to proceed with the installation activities:
· Quality
Control Procedure
· Method
Statement
· Inspection
Test Plan
· Check List
· Risk
Assessment
· Shop Drawing
Submittals related to work
-
Check all the delivered materials are inspected
and approved by the Consultant’s Engineer.
-
Ensure that the respective work area has been
cleared by previous trades for start-up installing the system.
-
Ensure that the installation of the material is
as per approved shop drawings, approved method statement, Manufacturer’s
recommendation, and prevailing quality standards.
-
Ensure the following checks are performed during
the installation progress:
-
Check all materials are as per approved submittal.
-
Check all Material are installed as per approved
shop drawings.
-
Check if coordinated with other services.
-
Check installation if it is carried out as per
approved method statement.
-
Check that the system checked and approved by Consultant.
-
Ensure WIRs are issued on time without delay.
(Min. 24 Hours notice for site inspection).
-
Ensure all inspection is performed as per
approved Inspection Test Plan.
- Check ITP, Check List, WIR, and NCR (if any) are signed off and cleared by the Consultant Engineer.
7.0 ATTACHMENTS
7.1 Method Statement
7.2 Inspection and Testing Plan
7.3 Check List for Installations
7.4 Risk Assessment
7.5 Attachments:
7.5.1 Manufacturer recommendations.
7.5.2 Emergency Evacuation Plan.
7.5.3 Technical Details.










