Linear vs Switch Mode Power Supplies
The Power Guy (Electrical
Engineer) focuses on modern switch-mode power
supplies and converters for powering Video Surveillance Camera.
Introduction
Linear power supplies were the
mainstay of power conversion until the late 1970’s when the first commercial
switch-mode became available. Now apart from very low power wall mount linear
power supplies used for powering consumer items like cell phones and toys,
switch-mode power supplies are dominant.
What are the differences and how do they work?
What are the differences and how do they work?
Linear power supplies have a bulky steel or iron laminated transformer. It
provides a safety barrier between for the high voltage
AC input and the low voltage DC output (Step Down Transformer). The transformer
also reduces and the AC input from typically 115V or 230VAC to a much lower
voltage, perhaps around 16-30VAC. The lower voltage AC is then rectified by two
or four diodes (Full Wave rectifier) and smoothed into low voltage DC by large
electrolytic capacitors. That low voltage DC is then regulated into the output
voltage by dropping the difference in voltage across a transistor or IC (the
shunt regulator).
Switch-mode supplies are a lot more complicated. The 115V or 230VAC voltage is rectified and smoothed by diodes and capacitors resulting in a high voltage DC. That DC is then converted into a safe, low voltage, high frequency (typically switching at 200kHz to 500kHz) voltage using a much smaller ferrite transformer and FETs or transistors. That voltage is then converted into the DC output voltage of choice by another set of diodes, capacitors and inductors. Corrections to the output voltage due to load or input changes are achieved by adjusting the pulse width of the high frequency waveform.
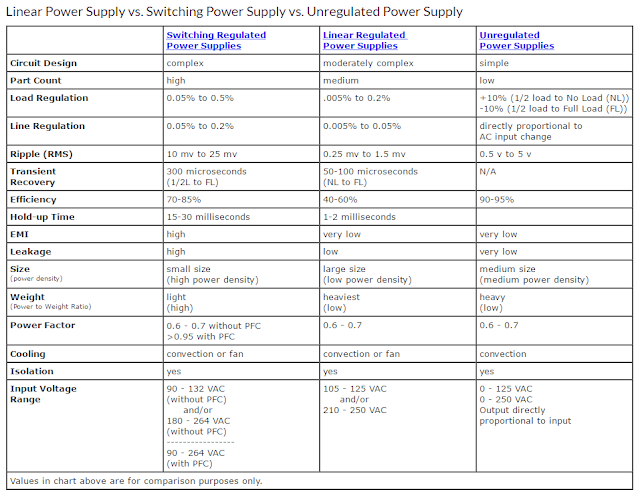
Comparisons of both technologies
Size: - A 50W linear power supply is typically 3 x 5 x 5.5”,
whereas a 50W switch-mode can be as small as 3 x 5 x 1”. That’s a size reduction
of 80%.
Weight: - A 50W linear weighs 4lbs; a corresponding switcher is 0.62 or less. As the power level increases, so does the weight. I personally remember a two-man lift needed for a 1000W linear.
Input Voltage Range: - A linear has a very limited input range requiring that the transformer taps be changed between different countries. Normally on the specification you will see 100/120/220/230/240VAC. This is because when the input voltage drops more than 10%, the DC voltage to the shunt regulator drops too low & the power supply cannot deliver the required output voltage. At input voltages greater than 10%, too much voltage is delivered to the regulator resulting in over heating. If a piece of equipment is tested in the US and shipped to Europe, Asia and Mexico in some cases, the transformer “taps” have to be manually changed. Forget to set the taps? The power supply will most certainly blow the fuse, or may well be damaged.
Weight: - A 50W linear weighs 4lbs; a corresponding switcher is 0.62 or less. As the power level increases, so does the weight. I personally remember a two-man lift needed for a 1000W linear.
Input Voltage Range: - A linear has a very limited input range requiring that the transformer taps be changed between different countries. Normally on the specification you will see 100/120/220/230/240VAC. This is because when the input voltage drops more than 10%, the DC voltage to the shunt regulator drops too low & the power supply cannot deliver the required output voltage. At input voltages greater than 10%, too much voltage is delivered to the regulator resulting in over heating. If a piece of equipment is tested in the US and shipped to Europe, Asia and Mexico in some cases, the transformer “taps” have to be manually changed. Forget to set the taps? The power supply will most certainly blow the fuse, or may well be damaged.
Most switch-mode supplies can operate anywhere in the world (85 to 264VAC), from industrial areas in Japan to the outback of Australia without any adjustment. The switch-mode supply is also able to withstand small losses of AC power in the range of 10-20 milliseconds without affecting the outputs. A linear will not. No one will care if the AC goes missing for 1/100th of a second when charging your cell phone, it will take 100 of these interruptions to delay the charge by one second. However, having your computerized equipment shutdown or reboot 100 times a day will cause a great deal of heartburn.
Efficiency:
A linear power supply because of its design will normally
operate at around 60% efficiency for 24V outputs, whereas a switch-mode is
normally 80% or more. Efficiency is a measure of how much energy the power
supply wastes. This has to be removed with fans or heat-sinks from the system.
As a quick note, in Europe, they are trying to limit those losses of all power supplies used by consumers particularly when operating in the “Off” mode (as many products are left plugged in 24 hours a day). Imagine 350 million power supplies eating up a couple watts. That equates to the output of a whole power station.
As a quick note, in Europe, they are trying to limit those losses of all power supplies used by consumers particularly when operating in the “Off” mode (as many products are left plugged in 24 hours a day). Imagine 350 million power supplies eating up a couple watts. That equates to the output of a whole power station.