6 Communication Protocols Used by IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT), is based on the networking of things. In a nutshell, Internet of Things is defined as a “proposed development of the Internet in which everyday objects have network connectivity, allowing them to send and receive data.”
The most
important thing here is connectivity among objects.
Research
companies like Gartner have predicted that Internet of Things will grow to
26 billion units in 2020. How will the devices be connected and what would
communication be like? How will wireless communication protocols evolve?
We can
boil down the wireless communication protocols into the following 6 standards:
1.
Satellite
2.
Wi-Fi
3.
Radio
Frequency (RF)
4.
RFID
5.
Bluetooth
6. NFC
In the following paragraphs, we will provide a brief overview and illustration of each of the Internet of Things communication techniques, their pros and cons, and their smartphone compatibilities.
1. Satellite
Satellite
communications enable cell phone communication from a phone to the next antenna
of about 10 to 15 miles. They are called GSM, GPRS, CDMA, GPRS, 2G / GSM, 3G,
4G / LTE, EDGE, and others based on connectivity speed.
In the
Internet of Things language, this form of communication is mostly referred
to as “M2M” (Machine-to-Machine) because it allows devices such as a phone to
send and receive data through the cell network.
Pros and Cons of Satellite Communication
Pros:
·
Stable connection
·
Universal
compatibility
Cons:
·
No direct
communication from smartphone to the device (It has to go through satellite)
·
High monthly cost
· High power consumption
Examples
of satellite connectivity would include utility meters that send data to a
remote server, commercials updated on digital billboards, or cars via Internet
connectivity.
Satellite is useful for communication that utilizes low data volumes, mainly for industrial purposes but in the changing near future where the cost of satellite communication is gradually falling, the use of satellite technology might become much more viable and interesting for consumers.
2. WiFi
WiFi is a
wireless local area network (WLAN) that utilizes the IEEE 802.11 standard
through 2.4GhZ UHF and 5GhZ ISM frequencies. WiFi provides Internet access to
devices that are within the range (about 66 feet from the access point).
Pros and Cons of WiFi
Pros:
·
Universal smartphone compatibility
·
Affordable
·
Well protected and controlled
Cons:
·
Relatively high power usage
·
Instability and inconsistency of WiFi
An example of WiFi connectivity would be Dropcam streaming live video via the local WiFi instead of streaming through a connected Ethernet LAN cable. WiFi is useful for many Internet of Things connections but such connections typically connect to an external cloud-server and are not directly connected to the smartphone. It is also not recommended for battery-powered devices due to its relatively high power consumption.
3. Radio Frequency (RF)
Radio
frequency communications are probably the easiest form of communication between
devices. Protocols like ZigBee or ZWave use
a low-power RF radio embedded or retrofitted into electronic devices and
systems.
Z-Wave’s
range is approximately 100 ft (30 m). The radio frequency band used
is specific to its country. For example, Europe has an 868.42 MHz SRD
Band, a 900 MHz ISM or 908.42 MHz band (United States), a
916 MHz in Israel, 919.82 MHz in Hong Kong, 921.42 MHz in the
regions of Australia/New Zealand) and 865.2 Mhz in India.
ZigBee is
based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. However, its low power consumption
limits transmission distances to a range of 10 to 100 meters.
Pros and Cons of Radio Frequency
Pros:
Low energy and simplicity for its technology is not
dependent on the new functionality of phones
Cons:
Radio frequency technology is not used by smartphones and
without a central hub to connect the RF devices to the internet, the devices
cannot be connected
An example
of radio frequency connectivity would be your typical television remote for it
uses radio frequency, which enables you to switch channels remotely. Other
examples include wireless light switches, electrical meters with in-home
displays, traffic management systems, and other consumer and industrial
equipment that requires short-range low-rate wireless data transfer.
Radio frequency communication protocol is useful for large deployments such as hotels where a high quantity of devices are required to be centrally and locally managed. However, in the near future, the technology might become increasingly outdated and be replaced by Bluetooth mesh networks.
4. RFID
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is the wireless use of electromagnetic fields to identify objects. Usually, you would install an active reader, or reading tags that contain a stored information mostly authentication replies. Experts call that an Active Reader Passive Tag (ARPT) system. Short-range RFID is about 10cm, but long-range can go up to 200m. What many do not know is that Léon Theremin invented the RFID as an espionage tool for the Soviet Union in 1945.
An Active
Reader Active Tag (ARAT) system uses active tags awoken with an interrogator
signal from the active reader. Bands RFID runs on: 120–150 kHz (10cm), 3.56 MHz
(10cm-1m), 433 MHz (1-100m), 865-868 MHz (Europe), 902-928 MHz (North America)
(1-12m).
Pros and Cons of RFID
Pros:
Does not require power
Established and widely used technology
Cons:
Highly insecure
Ongoing cost per card
Tags need to be present as identifier and be handed over
before
Not compatible with smartphones
Examples
include animal identification, factory data collection, road tolls, and
building access. An RFID tag is also attached to an inventory such that
its production
and manufacturing progress can be tracked through the assembly line.
As an illustration, pharmaceuticals can be tracked through warehouses. We
believe RFID technology will very soon be replaced by near-field communication (NFC)
technology in smartphones.
5. Bluetooth
Bluetooth
is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances
(using short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the ISM band from 2.4 to 2.485 GHz).
If you look at the frequencies it is actually the same as WiFi such that these
two technologies seem very similar. However, they have different uses. The 3
different styles of Bluetooth technology that are commonly talked about are:
Bluetooth: Remember
the days where you associate Bluetooth as a battery drainer and black hole?
Such Bluetooth is a heyday relic of a mobile past marked by a bulky cell phone.
Such Bluetooth technology is battery draining, insecure, and are often
complicated to pair.
BLE (Bluetooth 4.0,
Bluetooth Low Energy): Originally introduced by Nokia
and presently used by all major operating systems such as iOS, Android, Windows
Phone, Blackberry, OS X, Linux, and Windows 8, BLE uses fast, low energy usage
while maintaining the communication range.
iBeacon: It
is the trademark for a simplified communication technique based on Bluetooth
technology that Apple uses. What it actually is: a Bluetooth 4.0 sender that
transmits an ID called UUID, which is recognized by your iPhone. This
simplifies the implementation effort many vendors would previously face.
Moreover, even non-technically trained consumers can easily use iBeacons like
Estimote.com or other alternatives. Although different on a technical level,
iBeacon technology can be compared to NFC on an abstract level.
Bluetooth exists in many products, such as telephones, tablets, media players, robotics systems. The technology is extremely useful when transferring information between two or more devices that are near each other in low-bandwidth situations. Bluetooth is commonly used to transfer sound data with telephones (i.e., with a Bluetooth headset) or byte data with hand-held computers (transferring files). Bluetooth protocols simplify the discovery and setup of services between devices. Bluetooth devices can advertise all of the services they provide. This makes using services easier because relative to other communication protocols, it enables greater automation such as security, the network address, and permission configuration.
Comparison of Wifi
& Bluetooth
Wi-Fi and
Bluetooth are to some extent complementary in their applications and usage.
Wi-Fi
·
Access
point centered, with an asymmetrical client-server connection where it provides
all traffic routed through the access point.
·
Serves
well in applications where some degree of client configuration is possible and
high speeds are required e.g. network access through an access node
·
Ad-hoc
connections are possible with WiFi but not as easily with Bluetooth for Wi-Fi
Direct was recently developed to add a more Bluetooth-like ad-hoc functionality
Bluetooth
·
Symmetrical
between two Bluetooth devices
·
Serves well in simple applications where two
devices are needed to connect with minimal configuratione.g. headsets and
remote controls
·
Bluetooth access points do exist although they
are not common
Any
Bluetooth device in discoverable mode transmits the following
information on-demand:
·
Device
name
·
Device
class
·
List
of services
·
Technical
information (for example device features, manufacturer, Bluetooth specification
used, clock offset)
Pros & Cons of
Bluetooth
Pros:
·
Every smartphone has Bluetooth where
the technology is continuously being upgraded and improved through new hardware
·
Established and widely used technology
Cons:
·
Hardware capabilities change very fast
and will need to be replaced
·
Running on battery the lifetime of an
iBeacon is between 1month to 2 years
· If people switch off Bluetooth, there are issues in usage.
Bluetooth
technology mainly finds applications in the healthcare, fitness, beacons,
security, and home entertainment industries.
Bluetooth technology is definitely the hottest technology right now but it is many times overrated or misunderstood in functionality. If the application goes beyond fun you will have to dig deep in configuration and different settings as different phones react differently to Bluetooth.
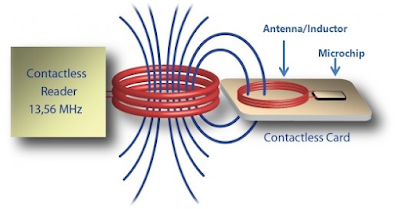
6. Near Field Communication (NFC)
Near-field
communication uses electromagnetic induction between two loop
antennas located within each other’s near field, effectively forming
an air-core transformer. It operates within the globally available and
unlicensed radio frequency ISM band of 13.56 MHz on ISO/IEC
18000-3 air interface and at rates ranging from 106 kbit/s to 424 kbit/s.
NFC involves an initiator and a target; the initiator actively generates
an RF field that can power a passive target (an unpowered chip called
a “tag”). This enables NFC targets to take very simple form factors such
as tags, stickers, key fobs, or battery-less cards. NFC peer-to-peer
communication is possible provided both devices are powered.
There are
two modes:
Passive
communication mode:
The initiator device provides a carrier field and the target device answers by
modulating the existing field. In this mode, the target device may draw its
operating power from the initiator-provided electromagnetic field, thus making
the target device a transponder.
Active
communication mode:
Both initiator and target device communicate by alternately generating their
own fields. A device deactivates its RF field while it is waiting for data. In
this mode, both devices typically have power supplies.
Pros & Cons of NFC
Pros:
·
Offers a low-speed connection with an
extremely simple setup
·
Can be used to bootstrap more
capable wireless connections
·
NFC has a short-range and supports
encryption where it may be more suitable than earlier, less private RFID
systems
Cons:
· Short-range might not be feasible in many situations for it is currently only available on new Android Phones and at Apple Pay on new iPhones
Comparison of BLE to
NFC
BLE and
NFC are both short-range communication technologies that are integrated into
mobile phones.
Speed: BLE
is faster
Transfer: BLE
has a higher transfer rate
Power: NFC
consumes less power
Pairing: NFC
does not require pairing
Time: NFC
takes less time to set up
Connection: Automatically
established for NFC
Data transfer rate: Max rate for BLE is 2.1 Mbits/s, max rate for NFC
is 424 kbits/s.
(NFC has a shortage range, a distance of 20cm, which
reduces the likelihood of unwanted interception hence it is particularly
suitable for crowded areas where correlating a signal with its transmitting
physical device becomes difficult.)
Compatibility: NFC is compatible with existing passive RFID (13.56
MHz ISO/IEC 18000-3) infrastructures
Energy protocol: NFC requires comparatively low power
Powered device: NFC works with an unpowered device.
NFC
devices can be used in contactless payment systems, similar to those currently
used in credit cards and electronic ticket smartcards, and it allows mobile
payment to replace or supplement these systems.
We believe that NFC will definitely replace the more insecure and outdated RFID cars where its use on smartphones will be limited to contact-only applications like payment, access, or identification.
Conclusion: And the IoT Winner Is?
It is very likely that the winner of these standards will be one that is available in many of the new devices and phones – otherwise, people would not use it. Today every smartphone has Bluetooth and WiFi. However, NFC is increasingly being implemented in new phones.
From our experience, a clear Internet of Things winner emerges when you have a very defined use-case. For example, if you’d like to transfer large amounts of files, WiFi is ideal. If you’d like to react on transient passengers, nothing tops Bluetooth. If you want quick, short-range interaction, NFC might be for you. Henceforth, the winning communication protocol really depends on your goals and your clearly defined use-case.
There will be many more providers of different standards – especially mesh-networked technologies such as GoTenna or mesh networked iBeacons.